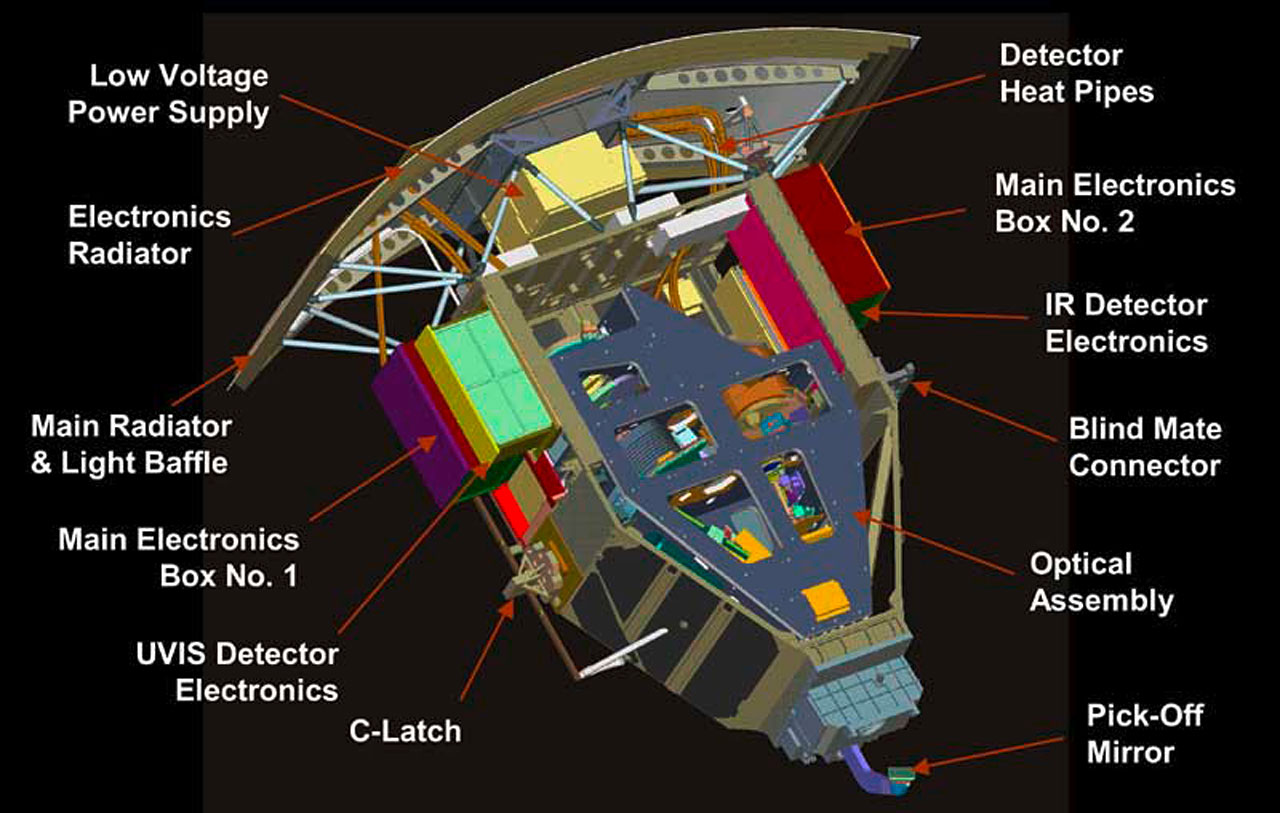
Hubble's Instruments: WFC3 - Wide Field Camera 3
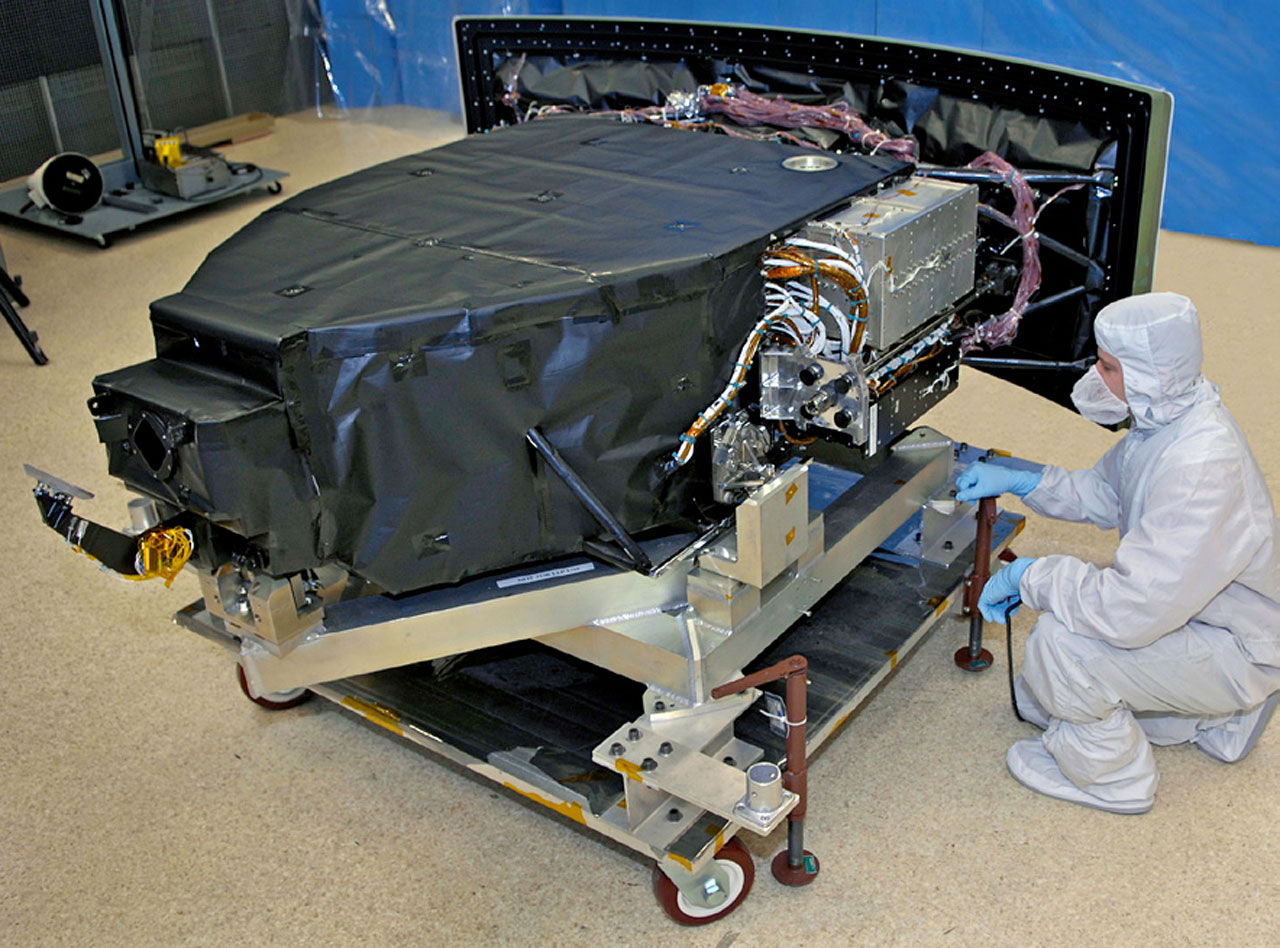
The installation of the new Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) during Servicing Mission 4 continued the pioneering tradition of previous Hubble cameras while incorporating critical improvements, clearing the way for a new voyage of discovery. Together with the new Cosmic Origins Spectrograph (COS), WFC3 leads the way to many more exciting scientific discoveries.
Overview
WFC3 is greatly enhancing the observational capabilities of Hubble. Compared to its predecessor, it offers improved resolution over a wider field of view. In terms of overall performance, it offers comparable performance to the ACS instrument, but over a wider range of wavelengths. The combination of these two elements — enhanced field of view and broader waveband — makes for a powerful instrument.
Technology
The instrument has two channels one for ultraviolet and visible light (UVIS) and the other for near infrared (NIR). In both cases, the detectors are the solid-state devices. For the UVIS channel a silicon-based CCD, similar to those found in digital cameras, is used. The similarities end there, however, as the CCD on WFC3 is a 16 megapixel, high sensitivity, low noise array. These high performance chips are made by e2V, a Uk based company, who specialise in the fabrication of large, high-performance, detector arrays for use in space. For the NIR channel, a 1 megapixel array made from the exotic material of mercuric cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) is used. The combination of these two technologies gives WFC3 its performance over a broad range of wavelengths. The table below reveals some of the key parameters for the instrument.
|
Parameter
|
UVIS Channel |
NIR Channel |
| Spectral range (nm) |
200-1000
|
850-1700
|
| Detector type |
Si
|
HgCdTe
|
| Detector array size (pixels) |
4096 x 4096
|
1024 x 1024
|
| Field of view (arcseconds) |
160 x 160
|
123 x 137
|
| Pixel size (arcsec) |
0.04
|
0.13
|
| Filter complement |
62
|
15
|
Science Goals
Observations in the ultraviolet and visible range will aim to address:
- Stellar Archaeology
- The distribution of galaxies at high redshift
Observations in the infrared range will aim to address:
- The highest redshift galaxies
- Water and ice on Mars and planetary moons
Panchromatic
- Galactic Evolution
- Star Birth, Death and Interstellar Medium
Development
The Hubble Program at the Goddard Space Flight Center, the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore and Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation in Boulder jointly developed the WFC3. A community-based Science Oversight Committee, led by Prof. Robert O’Connell of the University of Virginia, provided scientific guidance for the development.